Endocrine Disorders
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones that help control many important body functions, including the body's ability to change calories into energy that powers cells and organs. The endocrine system influences how your heart beats, how your bones and tissues grow, even your ability to make a baby. It plays a vital role in whether or not you develop diabetes, thyroid disease, growth disorders, sexual dysfunction, and a host of other hormone-related disorders.
Thyroid Disorder
Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in your neck, just above your collarbone.It is one of your endocrine glands, which make hormones. Thyroid hormones control the rate of many activities in your body. These include how fast you burn calories and how fast your heart beats. All of these activities are your body's metabolism.
Thyroidproblems include
- Goiter: enlargement of the thyroid gland.
- Hyperthyroidism: when your thyroid gland makes more thyroid hormones than your body needs.
- Hypothyroidism: when your thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormones Thyroid cancer
- Thyroid nodules: lumps in the thyroid gland
- Thyroiditis: swelling of the thyroid
- To diagnose thyroid diseases, doctors use a medical history, physical exam, and thyroid tests.
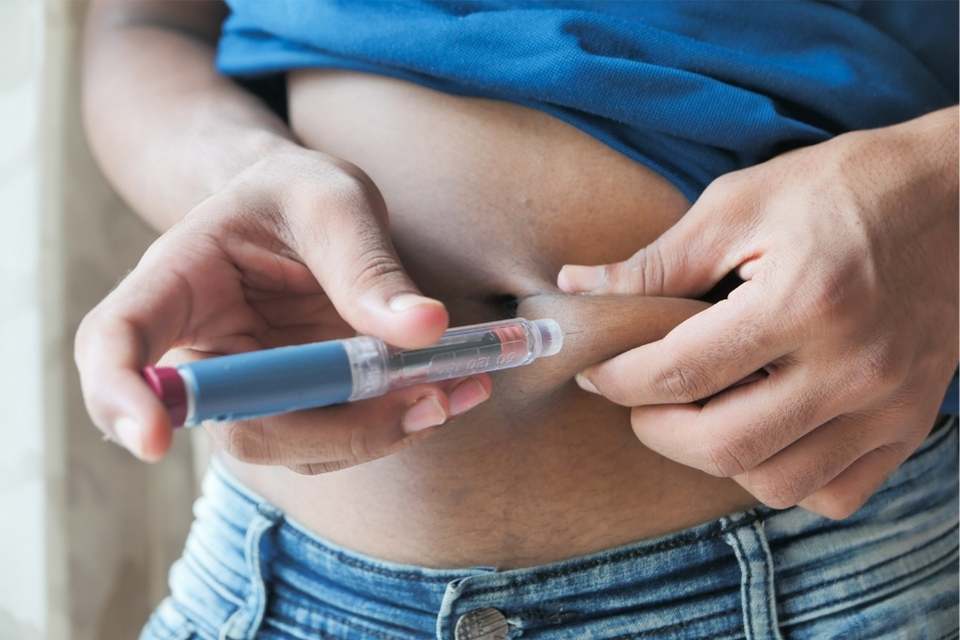
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus (DM), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased hunger. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced.
There are three main types of diabetes mellitus:-
Type 1 diabetes results from the pancreas's failure to produce enough insulin due to loss of beta cells. This form was previously referred to as "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (IDDM) or "juvenile diabetes”. The loss of beta cells is caused by an autoimmune response. The cause of this autoimmune response is unknown.
Type 2 diabetes begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to respond to insulin properly. As the disease progresses, a lack of insulin may also develop.This form was previously referred to as "non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (NIDDM) or "adult-onset diabetes”. The most common cause is a combination of excessive body weight and insufficient exercise.
Gestational diabetes is the third main form, and occurs when pregnant women without a previous history of diabetes develop high blood sugar levels.

Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to an extent that it may have a negative effect on health. People are generally considered obese when their body mass index (BMI), a measurement obtained by dividing a person's weight by the square of the person's height, is over 30 kg/m2; the range 25–30 kg/m2is defined as overweight. Obesity increases the likelihood of various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, osteoarthritis, and depression.
